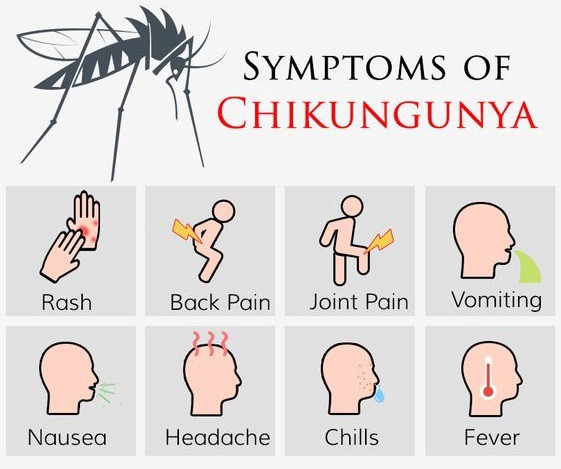
Chikungunya is a viral disease (genus Alphavirus) which is transmitted to humans by infected mosquitoes – including Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. The name chikungunya originates from a verb in the Kimakonde language, meaning 'to become contorted'. This refers to the 'stooped' appearance of those suffering with joint pain.